|
Table 10-2. Statistics of crossing in ERATO Kondoh project.
|
|
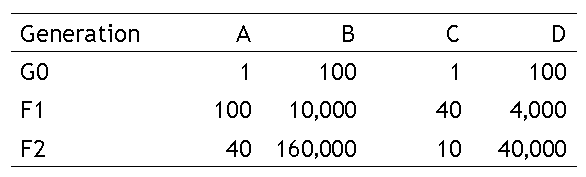
Simulation of statistics for a large-scale mutant screening.
A, population of fish/family; B, total population of fish that should be bred;
C, crossed pairs/family; D, total crossed pairs = families in the next generation.
If you perform mutagenesis to 100 males and raise 100 fish/F1 families, you need
the environment in which 10,000 fish can be raised. If you can cross at least
40 pairs/F1 families, you must cross 4,000 paired in F1 generation.
Then, you will get 4,000 F2 families. For (Pn > 94%), F2-C is 10 pairs.
For crossing 10 pairs at F2-C, you should raise 40 fish/families (F2-A).
Therefore, you need an environment in which 160,000 (= 4,000 x 40) fish can be
raised and 40,000 (= 4,000 x 10) pairs can be crossed.