|
Chapter 2
|
M2-1
|

|
Water flow into tanks
|
Medaka do better with a slow water flow in drops.
|
|
Producer: ODA
|
|
Time: 0'20
|
|
Filesize: 15.4 MB
|
M2-2
|

|
Washing the filtering materials
|
Stir the filtering bed with hands to clean it (once a month).
|
|
Producer: ODA
|
|
Time: 0'25
|
|
Filesize: 22.3 MB
|
M2-3
|

|
Washing the filtering mat
|
Remove the plastic pad and wash it with running tap water (every 2–4 weeks).
|
|
Producer: ODA
|
|
Time: 0'52
|
|
Filesize: 45.5 MB
|
M2-4
|

|
Cleaning the tanks
|
Polish the tank walls periodically with a small piece of filtering pad to remove algae and to obtain clear view of fishes. |
|
Producer: ODA
|
|
Time: 1'11
|
|
Filesize: 62.2 MB
|
M2-5
|

|
Removal of bottom debris I
|
Debris and algal mass at the bottom of the tanks can be removed using a handmade vacuum-cleaning device.
|
|
Producer: ODA
|
|
Time: 0'40
|
|
Filesize: 28.6 MB
|
M2-6
|

|
Removal of bottom debris II
|
Bottom debris can be removed manually with a pipette.
|
|
Producer: ODA
|
|
Time: 0'35
|
|
Filesize: 29.5 MB
|
M2-7
|

|
Removal of surface scum
|
White bacterial scum forming on the water surface without water flow must be removed using a sheet of Kimwipe before feeding every morning.
|
|
Producer: ODA
|
|
Time: 0'19
|
|
Filesize: 16.6 MB
|
|
Chapter 3
|
M3-1a
|

|
Mating behavior of medaka
(Failure to spawn)
|
A male fish attempts to mate a female but fails.
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 0'30
|
|
Filesize: 18.8 MB
|
M3-1b
|

|
Mating behavior of medaka
(Successful spawning)
|
The male is finally accepted by the female, and she spawns about 20 eggs.
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 1'09
|
|
Filesize: 45.3 MB
|
|
|
M3-2.
Methods of egg collection and related procedures.
|
M3-2a
|

|
Egg collection with a fish net
|
Fertilized eggs are collected from a female using a fish net.
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 0'39
|
|
Filesize: 40.6 MB
|
M3-2b
|

|
Transfer of the eggs into a dish
|
Collected eggs are handled with tweezers and are transferred into culture medium.
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 0'26
|
|
Filesize: 28.2 MB
|
M3-2c
|

|
Egg collection with a pipette
|
An alternative method using a pipette is less stressful for female fish, but more difficult. |
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 0'27
|
|
Filesize: 16.8 MB
|
M3-2d
|

|
Separation mating for scheduled spawning
|
The spawning time can be controlled by separating the male and female with a thin plastic plate.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 0'47
|
|
Filesize: 35.4 MB
|
|
|
M3-3.
Methods of egg separation
|
M3-3a
|

|
Egg separation with fingers
|
Attaching filaments can be removed by pressing and rotating the egg cluster on a Petri dish with fingers.
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 0'34
|
|
Filesize: 24.4 MB
|
M3-3b
|

|
Egg separation with tweezers I
|
Attaching filaments can be removed with tweezers. The microscopic view is shown in M3-3c.
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 0'36
|
|
Filesize: 25.4 MB
|
M3-3c
|

|
Egg separation with tweezers II
|
This method is easy and quick for separating a large number of eggs (Microscopic view of M3-3b).
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 0'34
|
|
Filesize: 26.8 MB
|
M3-3d
|
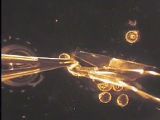
|
Egg separation with scissors
|
Microscopic view of removal of attaching filaments with scissors. This method can be applied to a small number of eggs.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 0'32
|
|
Filesize: 19.7 MB
|
M3-4
|

|
Two methods of gathering eggs to the center of a Petri dish
|
To examine eggs in a Petri dish under a stereomicroscope, the eggs can be gathered by rotating the dish or by stirring with a transfer pipette.
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 0'26
|
|
Filesize: 19.8 MB
|
|
Chapter 4
|
M4-1
|

|
Pasteurization of the eggs with bleaching solution
|
When you receive eggs from other laboratories, it is necessary to pasteurize the eggs to prevent infectious diseases.
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 1'29
|
|
Filesize: 84 MB
|
M4-2a
|

|
Sperm freezing
|
Procedures for cryopreservation of medaka sperm are presented.
|
|
Producer: SASADO
|
|
Time: 3'12
|
|
Filesize: 185 MB
|
M4-2b
|

|
Sperm motility I
(non frozen sperm)
|
The motility and density of sperm are checked in each sperm suspension under a phase contrast microscope before freezing.
|
|
Producer: SASADO
|
|
Time: 0'04
|
|
Filesize: 18.8 MB
|
|
|
M4-3.
Methods of artificial insemination and related procedures
|
M4-3a
|
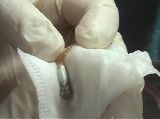
|
Collection of unfertilized eggs
|
Unfertilized eggs can be collected from an anaesthetized female by squeezing her abdomen
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 0'47
|
|
Filesize: 38.9 MB
|
M4-3b
|

|
Selection of eggs for artificial insemination
|
Non-activated eggs suitable for artificial insemination can be clearly distinguished from “activated eggs.”
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 1'09
|
|
Filesize: 66.3 MB
|
M4-3c
|

|
Sperm-thawing steps of artificial insemination
|
Procedures for thawing of medaka sperm are presented.
|
|
Producer: SASADO
|
|
Time: 1'39
|
|
Filesize: 81.3 MB
|
M4-3d
|

|
Insemination of unfertilized eggs with thawed sperm
|
Procedures for insemination of unfertilized eggs with thawed sperm are presented. |
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 1'37
|
|
Filesize: 129 MB
|
M4-3e
|

|
Motility of thawed sperm
|
The motility and density of sperm are checked immediately after insemination.
|
|
Producer: SASADO
|
|
Time: 0'04
|
|
Filesize: 30.5 MB
|
M4-4
|

|
Infertile mating
|
The infertile mating method is highly practical to collect unfertilized eggs for artificial insemination.
|
|
Producer: KAMEI
|
|
Time: 1'12
|
|
Filesize: 76.7 MB
|
|
Chapter 6
|
M6-1
|

|
Embryonic development from fertilization to hatching
|
This movie shows embryonic development from fertilization to hatching.
|
|
Producer: JST ERATO/SORST Kondo project
|
|
Time: 1'28
|
|
Filesize: 48.0 MB
|
|
|
M6-2.
Heart beat of developing embryos (stages 24 to 36)
|
M6-2a
|
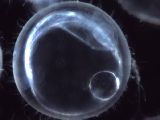
|
Heart development I
|
Stage 24, right lateral view. The heart tube has initiated a rhythmic beat by this stage. |
|
Producer: MURATA
|
|
Time: 0'15
|
|
Filesize: 10.4 MB
|
M6-2b
|
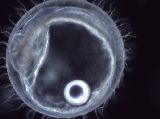
|
Heart development II
|
Stage 24–25, left lateral view. Heart tube development continues.
|
|
Producer: MURATA
|
|
Time: 0'15
|
|
Filesize: 11.3 MB
|
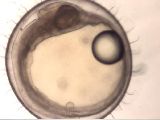
M6-2c
|
|
Heart development III
|
Stage 25, right lateral view.
|
|
Producer: MURATA
|
|
Time: 0'15
|
|
Filesize: 10.1 MB
|
M6-2d
|

|
Heart development IV
|
Stage 26, ventral view. |
|
Producer: MURATA
|
|
Time: 0'15
|
|
Filesize: 7.66 MB
|
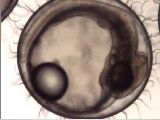
M6-2e
|
|
Heart development V
|
Stage 28, right lateral view. |
|
Producer: MURATA
|
|
Time: 0'15
|
|
Filesize: 11.9 MB
|
M6-2f
|

|
Heart development VI
|
Stage 28–29, ventral view. |
|
Producer: MURATA
|
|
Time: 0'15
|
|
Filesize: 7.46 MB
|
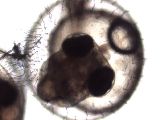
M6-2g
|
|
Heart development VII
|
Stage 35–36, head and beating heart. |
|
Producer: MURATA
|
|
Time: 0'15
|
|
Filesize: 12.3 MB
|
M6-3
|

|
Removing short villi on the egg envelope
|
To obtain a clear view, remove short villi from the surface of egg envelope by rolling on a fine sandpaper.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 1'05
|
|
Filesize: 60.6 MB
|
|
Chapter 7
|
|
M7-1.
Methods of microinjection and related procedures
|
M7-1a
|

|
Microinjection using an upright microscope
|
This movie shows the flow of microinjection using an upright microscope.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 2'19
|
|
Filesize: 156 MB
|
M7-1b
|

|
Separation mating for scheduled spawning
|
To inject into 1-cell stage embryo, fertilized eggs must be collected
and injected within a half hour after mating. Separation mating method
is highly practical to control the time of spawning.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 0'47
|
|
Filesize: 35.4 MB
|
M7-1c
|

|
Preparation of eggs for microinjection
|
Long attaching filaments should be removed before microinjection.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 0'30
|
|
Filesize: 22.7 MB
|
M7-1d
|

|
Adjusting the egg orientation for microinjection
|
Prior to microinjection, the cytoplasm is oriented to where the needle will arrive, and the egg should be fixed on the egg holder.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 0'47
|
|
Filesize: 42.7 MB
|
M7-1e
|

|
Opening the tip of the microinjection needle
|
It is necessary to break and open the tip of microinjection needle before use.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 0'22
|
|
Filesize: 16.1 MB
|
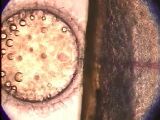
M7-1f
|
|
Microinjection into 1-cell cytoplasm
|
This movie shows injection of solution into 1-cell cytoplasm.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 0'37
|
|
Filesize: 43.3 MB
|
M7-2
|

|
Making needle using a needle puller
|
Horizontal and vertical type of pullers can be used to make injection needles.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 1'09
|
|
Filesize: 53.4 MB
|
M7-3
|

|
Sharpening the end of injection needle
|
Needle with a sharpened tip is sometimes preferable.
|
|
Producer: KINOSHITA
|
|
Time: 1'23
|
|
Filesize: 69.7 MB
|
|
Chapter 10
|
M10-1
|

|
Single cell labeling
|
Movement of individual cells in an early embryo is shown. The cells move, divide, and form neural compartments during neurogenesis.
|
|
Producer: HIROSE
|
|
Time: 0'42
|
|
Filesize: 11.8 MB
|
M10-2a
|
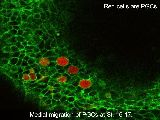
|
Imaging for living embryo I
|
Time-lapse imaging of the medial migration of primordial germ cells at stages 16–17.
|
|
Producer: SAITO
|
|
Time: 0'14
|
|
Filesize: 12.8 MB
|
M10-2b
|
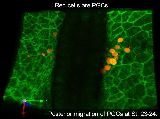
|
Imaging of living embryo II
|
Time-lapse imaging of the posterior migration of primordial germ cells at stages 23–24.
|
|
Producer: SAITO
|
|
Time: 0'11
|
|
Filesize: 9.34 MB
|
M10-3
|

|
ENU Mutagenesis
|
This movie shows the flow of ENU mutagenesis.
|
|
Producer: JST ERATO/SORST Kondo project
|
|
Time: 2'02
|
|
Filesize: 35.6 MB
|















































