|
|
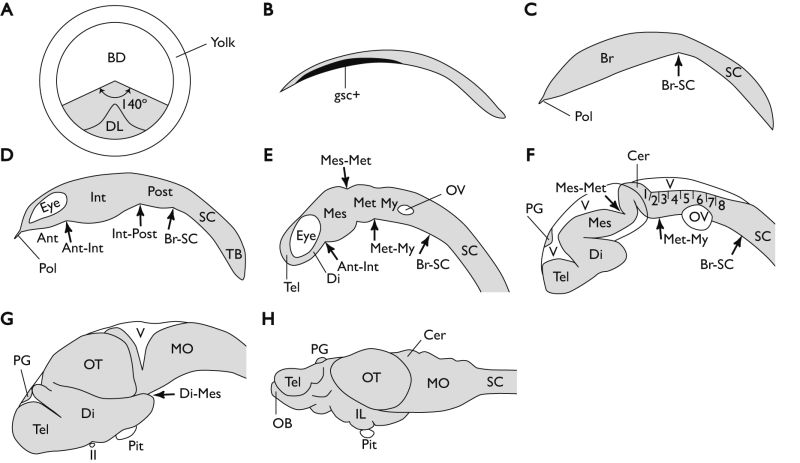
Figure 6-9. Schematic diagram showing the development of the medaka brain, modified from Kage et al. (2004) and Ishikawa (1997). A Animal polar view of the embryo at the gastrula step (stage 13). All future neural cells are present within a dorsal 140° sector of the blastoderm, as shown by gray shading. B Lateral view of the embryonic body at the gastrula step (stage 16). The goosecoid-expressing area is shown in black. C Lateral view of the embryonic body at the gastrula step (stage 16/17). The goosecoid-expressing cells begin to bulge ventrally, and later gives rise to the brain. The polster, which develops into the hatching gland, is located around the rostral tip of the brain. D Lateral view of the embryonic body at the neurula step (stage 18). The brain rudiment begins to show three subdivisions: the anterior, intermediate, and posterior brain vesicles. E Lateral view of the embryonic body at the neural rod step (stage 21). The anterior brain vesicle develops into the telencephalon and rostral diencephalon. The intermediate brain vesicle gives rise to the caudal diencephalon, mesencephalon, and metencephalon. The posterior brain vesicle develops into the myelencephalon. F Lateral view of the embryonic body at the neural tube step (stage 25). The cephalic flexure appears in the diencephalon. This results in the ventral diencephalon being covered by the dorsal diencephalon and mesencephalon. The eight rhombomeres become visible. G Lateral view of the brain at the late embryonic brain step. The dorsal mesencephalon has expanded dorsolaterally to form the optic tectum. H Lateral view of the brain at the larval brain step. The arrows indicate the subdivision boundaries. Rostral is to the left in (B–H). Ant, anterior brain vesicle; BD, blastoderm; Br, brain; Cer, cerebellum; Di, diencephalon; DL, dorsal lip (embryonic shield); gsc+, goosecoid-expressing area; IL, inferior lobe; Int, intermediate brain vesicle; Mes, mesencephalon; Met, metencephalon; MO, medulla oblongata; My, myelencephalon; OB, olfactory bulb; OT, optic tectum; OV, otic vesicle; PG, pineal grand; Pit, pituitary; Pol, polster; Post, posterior brain vesicle; SC, spinal cord; TB, tail bud; Tel, telencephalon; V, ventricle; II, optic nerve. (Kage et al., 2004. Reproduced with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.) |