> Large size
|
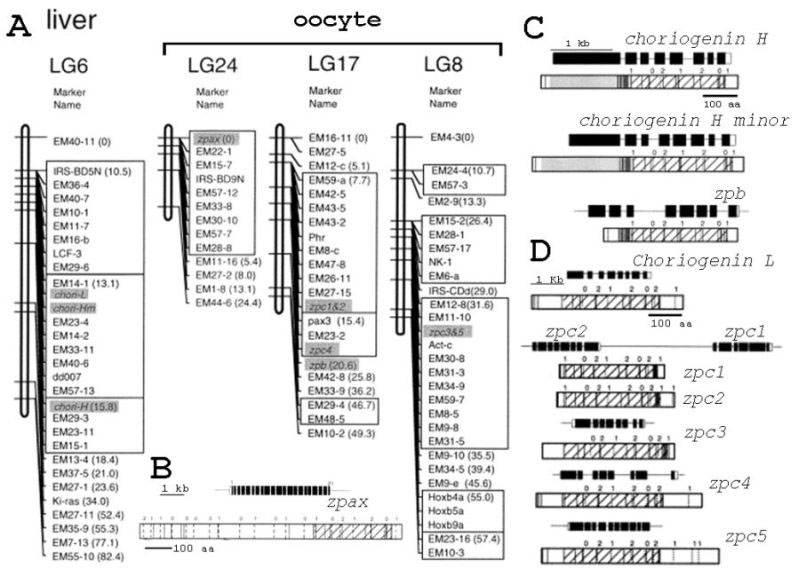
Figure 3-7. A genetic linkage map of medaka egg envelope genes (a) and comparison of medaka zpax (A), choriogenin H and choriogenin H minor (zpb) (B); and choriogenin L (zpc) products and their known genomic organization (C). (A) Map distance from the top locus is shown in parentheses by centimorgans. (B) the predicted gene product and genomic organization of medaka zpax (AF128807). For the proteins, vertical solid lines represent conserved cysteine residues between medaka and Xenopus zpax product or those among mammalian zpa products (according to Harris et al., 1994). Dotted square at C-terminus of the ZPA product represents the transmembrane domain. (C) The predicted gene product and genomic organization of medaka choriogenin. H, choriogenin. H minor and zpb. The light gray squares in N-terminal regions of the gene products of medaka choriogenin H (D89609), and choriogenin H minor (AB025967) represent repetitive domains. Medaka, zpb (AF128808) products do not have the repetitive domain. Dark gray squares represent trefoil domains. (D) the predicted gene product and genomic organization of medaka choriogenin L (D38630), zpc1~5 (AF128809, AF128810, AF128811, AF128812 and AF128813). B, C, and D; are drawn to scale. For the genes, each square represents individual exons; coding regions are closed and untranslated regions are open. For proteins, cysteine residues in each protein are shown in the vertical lines. The dashed vertical lines represent position of the introns. The numbers near the dashed vertical lines show positions of introns in junction codons. 0 means that introns are located between codons. 1 or 2 means that introns are located after the first or second nucleotides of the codons at the junctions. Hatched regions are ZP domains (arbitrarily defined between the first and the last cysteine residues). (Modified from Kanamori et al., 2003.) |